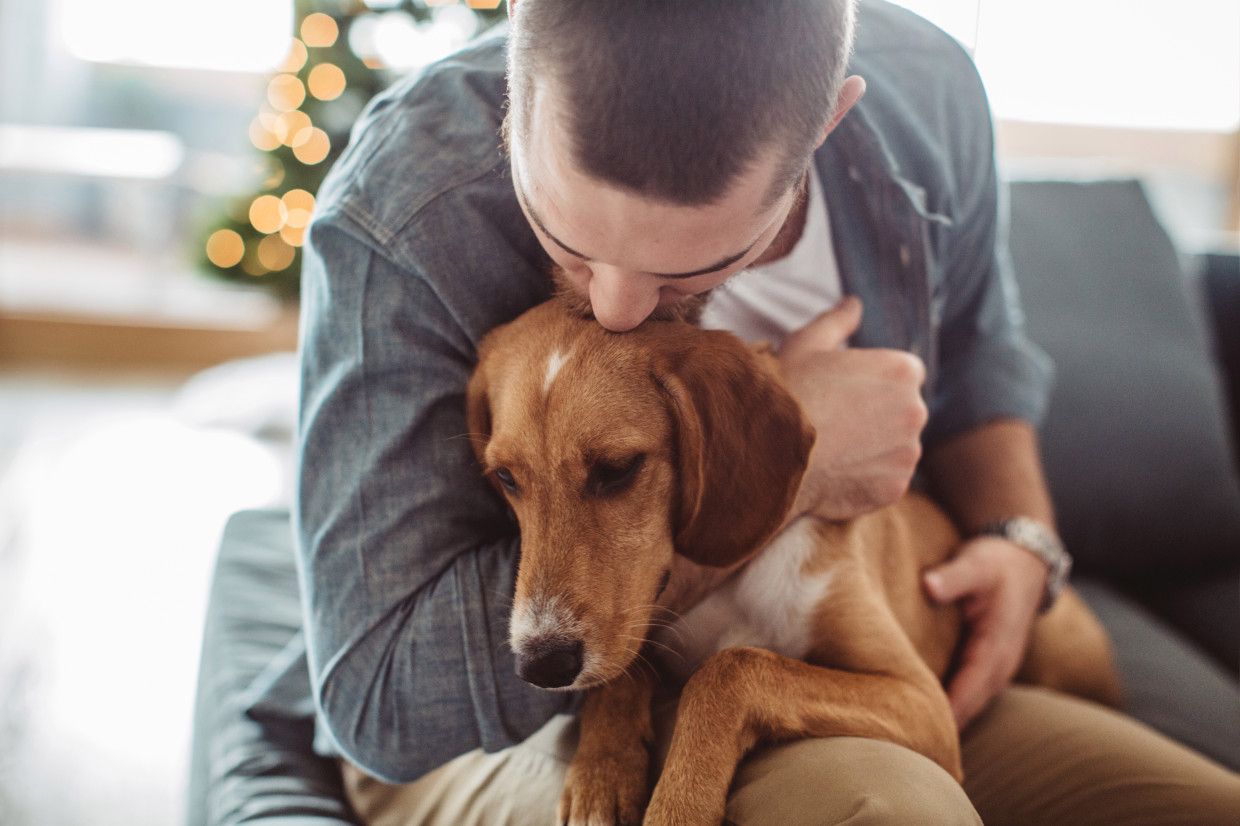

Dogs And Their Mental Health
Dogs, like humans, can experience mental health issues. While dogs cannot communicate their emotions and feelings in the same way we do, they exhibit certain behaviors that can indicate their mental well-being. Here are some common mental health concerns in dogs and what animal owners can do:
- Anxiety and Fear: Dogs may experience anxiety or fear in response to various situations, such as separation anxiety, loud noises, or new environments. Signs include excessive panting, pacing, trembling, restlessness, destructive behavior, or withdrawal. To help alleviate anxiety, provide a safe and secure environment, establish a routine, and consider desensitization training or consulting a professional trainer or veterinarian for behavioral therapy or medication if necessary.
- Depression: Dogs can experience depression due to major life changes, loss of a companion, or prolonged periods of loneliness or boredom. Signs may include decreased appetite, lethargy, withdrawal, decreased interest in activities, or changes in sleep patterns. To support a depressed dog, ensure regular exercise, mental stimulation, social interaction with humans and other animals, and consider introducing new toys, activities, or even a new companion (if appropriate) to help lift their spirits.
- Compulsive Behaviors: Dogs may develop compulsive behaviors like excessive licking, chewing, tail chasing, or repetitive movements. These behaviors can be a sign of stress or boredom. Encourage mental and physical stimulation through regular exercise, puzzle toys, and interactive play. Create a calm and structured environment, and consult with a veterinarian or animal behaviorist for guidance on behavior modification techniques or medication if necessary.
- Aggression: Aggressive behavior in dogs can be a result of fear, anxiety, frustration, or territoriality. It’s crucial to address aggression promptly and seek professional guidance from a certified dog trainer or veterinary behaviorist. They can assess the underlying causes and provide training techniques, behavior modification strategies, or medication if required.
- Cognitive Dysfunction: As dogs age, they may develop cognitive dysfunction, similar to human dementia. Signs include disorientation, confusion, changes in sleep patterns, decreased social interaction, and house soiling. Maintain a consistent routine, provide mental stimulation through puzzle toys or training exercises, ensure regular veterinary check-ups, and consult a veterinarian for potential treatment options.
Remember, if you notice any concerning changes in your dog’s behavior or suspect they may be experiencing mental health issues, it’s important to consult with a veterinarian or animal behaviorist. They can provide a proper diagnosis, develop a tailored treatment plan, and guide you through strategies to support your dog’s mental well-being.










Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.